Viking warriors, often romanticized for their fierce seafaring raids, also found lucrative opportunities as mercenaries across Europe.
During the Battle of the River Elbe in 1015, Norse mercenaries played a crucial role, showcasing their combat prowess and strategic mind.
These Norse warriors blended seamlessly into the various military fronts of the time, bringing with them the martial skills and fearless tactics honed during the Viking Age.
The Norse mercenaries’ involvement at the River Elbe was not merely a historical footnote but a significant display of their impact on European warfare.
Known for their use of heavy and effective weaponry, such as battle-axes and swords, they were a formidable addition to any army. Their presence was a testament to the far-reaching influence of Viking culture, as these warriors often served lords and kings far beyond Scandinavia.
The allure of the Vikings as hired swords lay in their reputation for unwavering loyalty and effectiveness in battle.
Their participation in conflicts like the Battle of the River Elbe illustrates how these Norse soldiers of fortune could turn the tide of battle with their ferocity and tactical acumen.
Engaging these fierce warriors was a strategic move for any leader looking to gain an upper hand during the volatile period of the Viking Age.
Origins and History of Norse Warriors

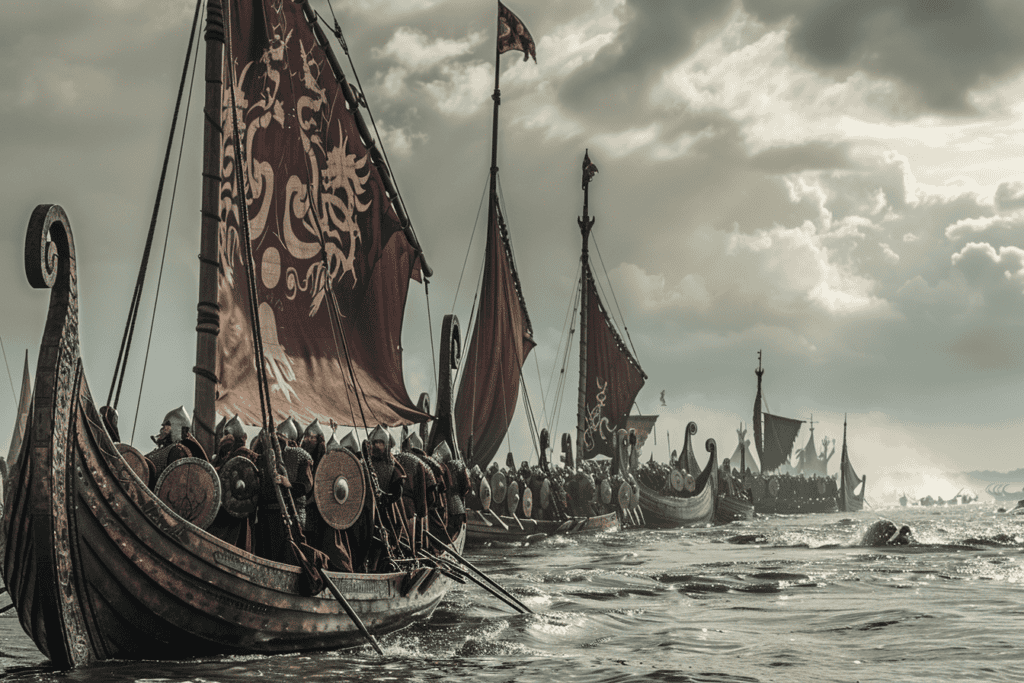
Norse warriors, commonly referred to as Vikings, originated from the Scandinavian countries of modern-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. Viking society was heavily influenced by seafaring, which enabled them to embark on long voyages.
During the 8th century, the Viking Age began, marked by extensive raids on coastal Europe. These Norsemen utilized advanced naval technology and seafaring skills to establish a reputation as formidable raiders and traders.
The Viking longships, known for their speed and shallow draft, allowed them to navigate both open seas and rivers.
This mobility was crucial in their ability to strike swiftly and retreat just as quickly.
Meanwhile, Norse society also placed a high value on warrior culture, with young men often training for combat from a young age.
Expansion Throughout Europe
As the Viking Age progressed, Norse warriors expanded their reach throughout Europe. They didn’t just raid; they established settlements and integrated into various societies.
The Norse began to set up colonies in places like England, Ireland, and Iceland. They founded the city of Dublin and even reached as far as the Mediterranean and the Middle East.
With their strategic mobility and effective use of ships, the Vikings exerted influence over vast areas, including the British Isles, Frankish territories, and even parts of modern-day Russia (Rus).
In these regions, they engaged in trade, established trade routes, and often demanded tribute from local rulers. This expansion not only resulted in cultural exchanges but also in the spread of Norse technology and warfare techniques.
Vikings as Mercenaries
By the late Viking Age, Norse warriors began offering their services as mercenaries. Their reputation for combat prowess made them sought after by various European rulers.
One notable instance was their involvement in the Battle of the River Elbe in 1015. Here, Norse mercenaries played a crucial role, showcasing their strategic and combat skills.
Kings and nobles would often hire Vikings to bolster their forces, leveraging their expertise in warfare and navigation.
These Norse mercenaries could be found serving in the Byzantine Empire’s elite Varangian Guard or fighting in the civil wars of European kingdoms.
Their transition from raiders to professional soldiers marks a significant evolution in their role, reflecting their adaptability and enduring martial legacy.
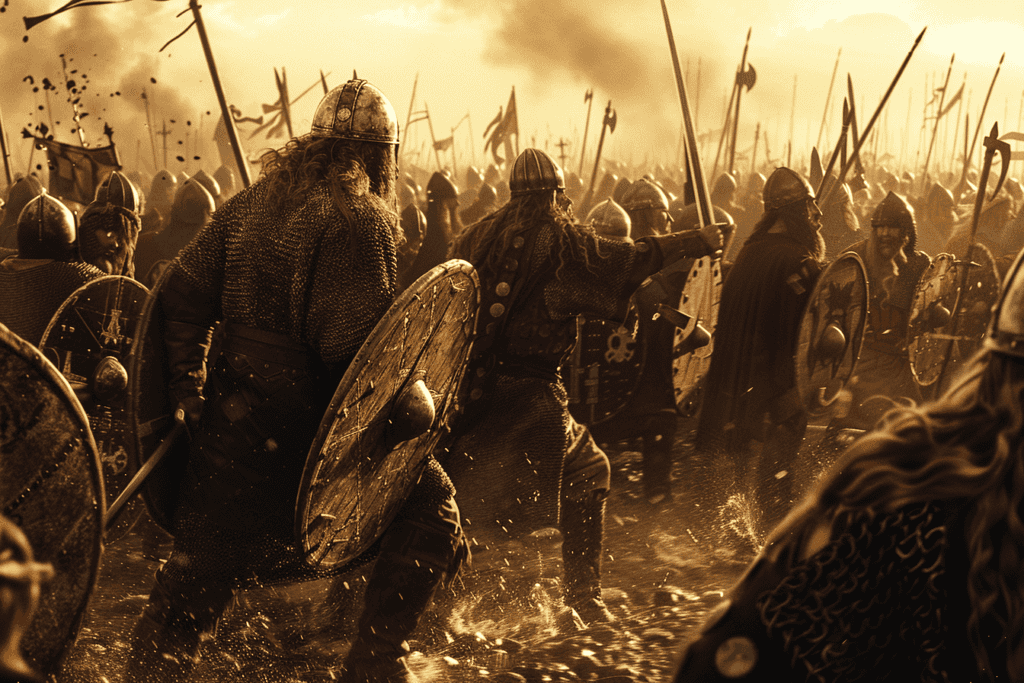
Military Tactics and Warfare of Vikings

The Vikings were known for their strategic mobility, naval prowess, and strong kinship bonds. Their heavy use of ships and unique battle tactics left an indelible mark on warfare during the Viking Age.
Vikings excelled in sudden raids facilitated by their longships.
These vessels, with shallow-draft hulls, allowed them to cross seas and navigate rivers stealthily, appearing out of nowhere.
This element of surprise was crucial in many raids, such as the infamous attack on Lindisfarne in 793 CE. Their ability to strike swiftly and disappear quickly made them formidable raiders.
They were also renowned for their combat skills and formidable appearance.
The shield-wall (skjaldborg) was a key formation where warriors stood shoulder to shoulder with interlocked shields.
Well-armored fighters formed the front lines, using high-quality shields, swords, axes, and sometimes spears. Helmets and chainmail were also common, providing additional protection on the battlefield.
Kinship and loyalty played vital roles in Viking military structures. Warriors fought not just for plunder but to uphold family honor and loyalty to their chieftain.
This strong sense of kin and loyalty enhanced their battlefield coordination, ensuring they fought cohesively as a unit.
Additionally, their familial bonds provided a robust support system, reinforcing their strength and resolve during conflicts.
Vikings’ Role in European Power Dynamics
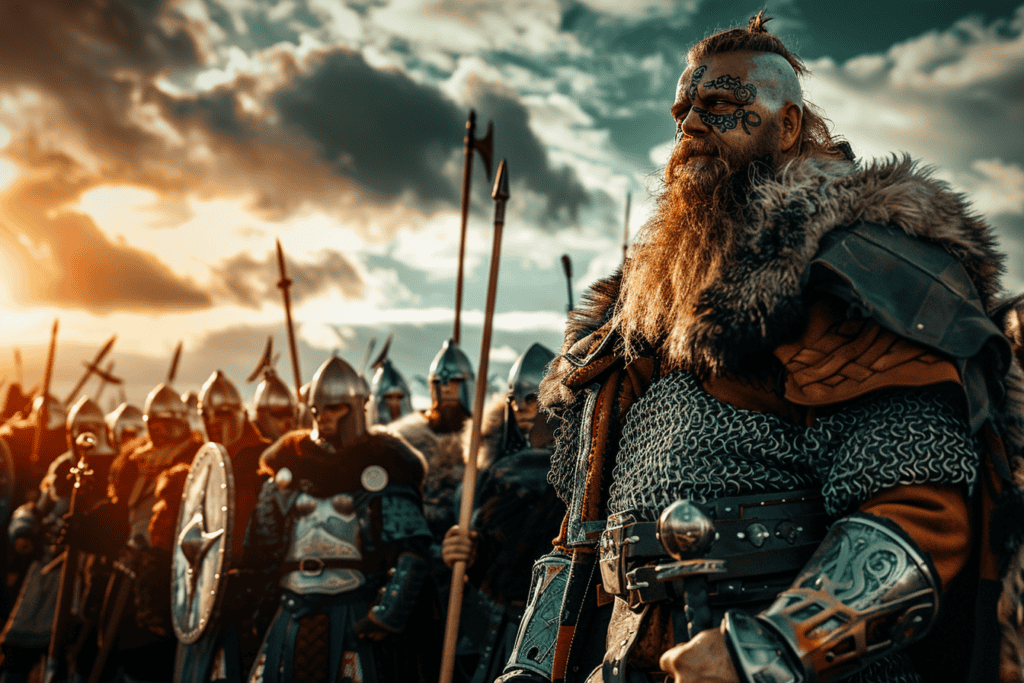

Vikings played a key role in shaping European power dynamics through their various alliances with local rulers and their influence beyond the Scandinavian Peninsula. Their prowess as warriors and raiders allowed them to exert control and instill fear across the continent.
Viking warriors often formed strategic allegiances with European kings and rulers. They were known for offering their services as mercenaries, defending territories, and participating in local conflicts.
This relationship was mutually beneficial; Vikings received gold and land, while kings secured skilled fighters.
In England, Viking warriors notably supported King Knut, helping him solidify power and control over vast regions. In return, they were granted significant land holdings.
By serving Christian rulers, Vikings not only enriched themselves but also gained prestige, integrating into the evolving Christianized European society.
Cultural and Religious Integration
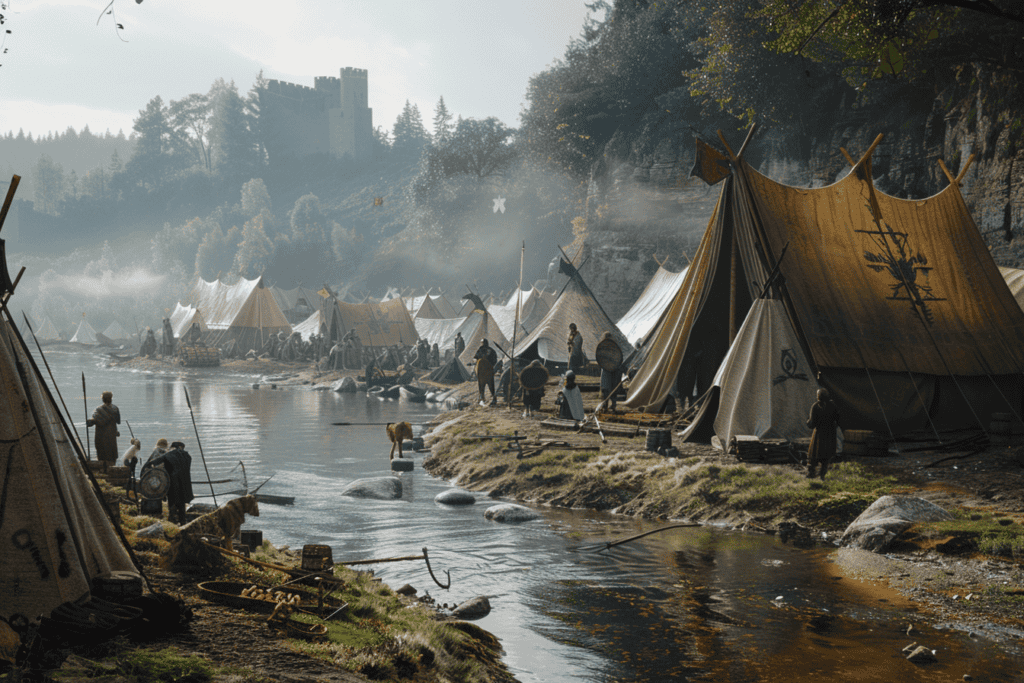

The Christianization of Scandinavia significantly influenced Viking society.
As Norse mercenaries traveled, they encountered Christian practices and institutions, such as churches and monasteries. For example, many Vikings who fought in the Battle of the River Elbe were influenced by the spread of Christianity from regions like Iona.
As they adopted Christianity, these warriors brought new religious practices back home. This transition altered their rituals and societal structures.
Baptism began to replace traditional rites, and churches emerged in Norse communities.
Icelandic sagas often depict this transformative period, illustrating the complex integration of new Christian beliefs with traditional Norse values.








Add Comment