The Battle of Maldon was one of the most significant conflicts between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons.
It took place in the year 991 AD in Essex, England, and is remembered as a fierce encounter that saw the Anglo-Saxons ultimately defeated.
The battle has been immortalized in an Old English heroic poem that recounts the bravery and sacrifice of the English soldiers.
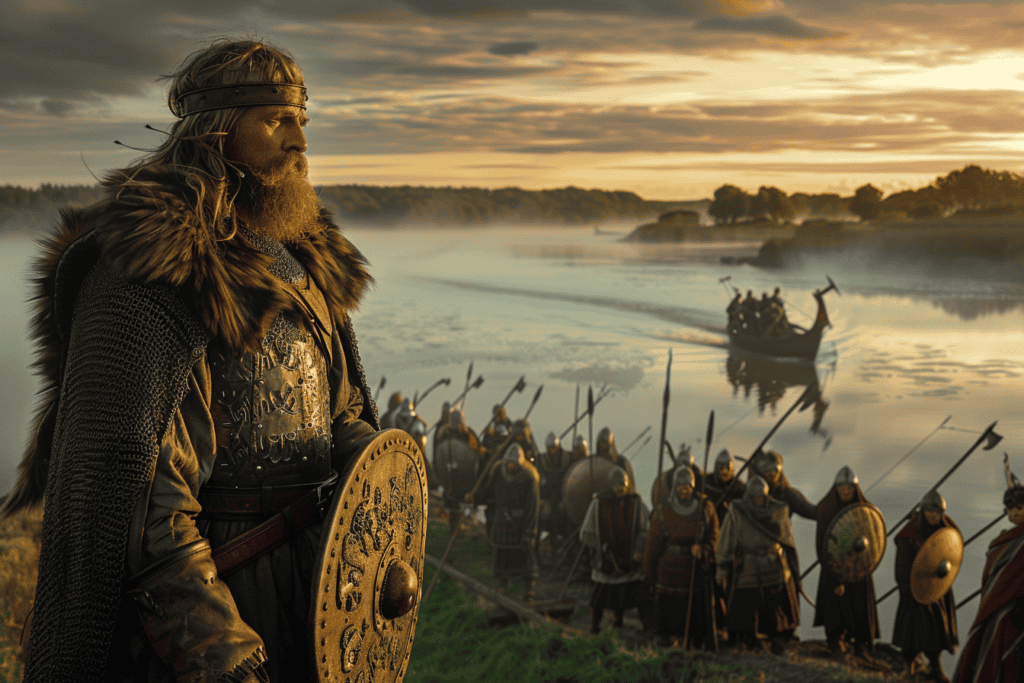
The conflict arose when a Viking army led by Olaf Tryggvason attempted to invade England. They were met by a small group of Anglo-Saxon soldiers led by Byrhtnoth, the ealdorman of Essex.
The Anglo-Saxons were outnumbered and outgunned, but they refused to back down and fought valiantly to defend their homeland.
The battle lasted for several hours, and in the end, the English suffered a devastating defeat.
Despite their loss, the Anglo-Saxon soldiers were celebrated as heroes for their bravery and loyalty to their country. The Battle of Maldon remains an important event in English history and is often studied as an example of the courage and resilience of the Anglo-Saxon people.
Historical Context – Viking Raids in Britain
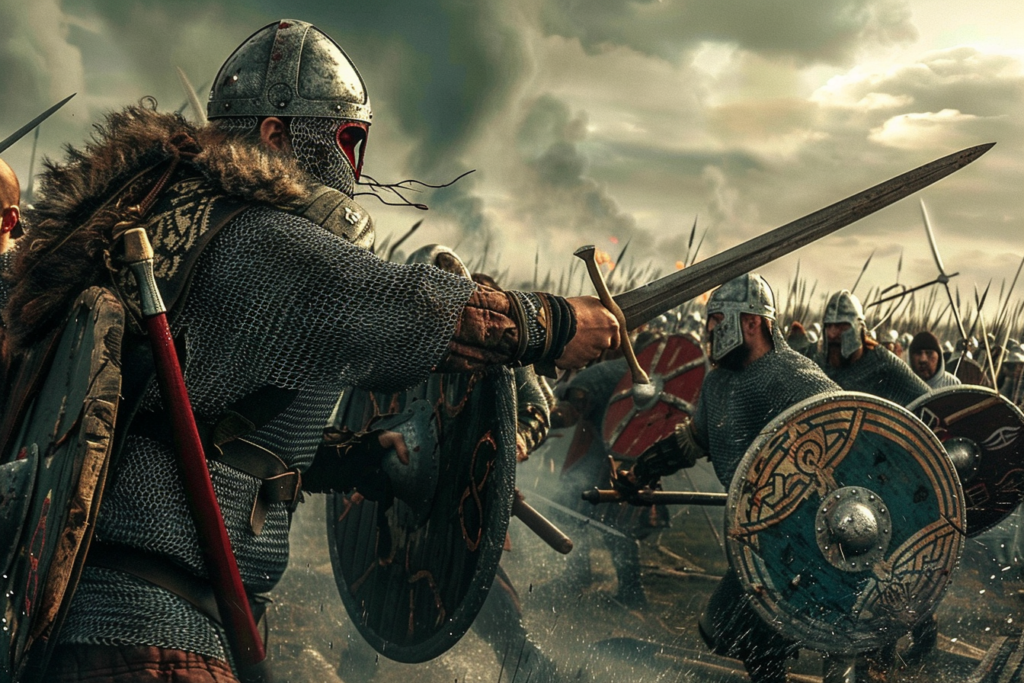

The Viking raids in Britain began in the late 8th century, with the infamous raid on the monastery at Lindisfarne in 793 AD.
These raids were swift and surprise attacks from their fast, shallow-draft longships. The Vikings were known for their fearsome reputation as warriors and their ability to move quickly and efficiently.
Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms
The Anglo-Saxon kingdoms faced significant challenges in the initial stages of Viking incursions into Britain. The Anglo-Saxons inhabited the area now known as the modern-day United Kingdom, and they had established several small kingdoms.
These kingdoms were vulnerable to Viking raids, and the Anglo-Saxons struggled to defend themselves against these attacks.
Rise of the Danelaw
The Vikings were successful in their raids on Britain, and they established a significant presence in the country.
They formed an area known as the Danelaw, which included parts of Northumbria and East Anglia. The Vikings were able to exert their influence over these areas, and they were able to establish a foothold in the country.
The Danelaw was a significant turning point in the history of Britain. It marked the beginning of a new era, and it had a profound impact on the country’s culture and society.
The Vikings brought with them their own language, Old Norse, which had a significant impact on the development of the English language.
Prelude to the Battle – Political Landscape
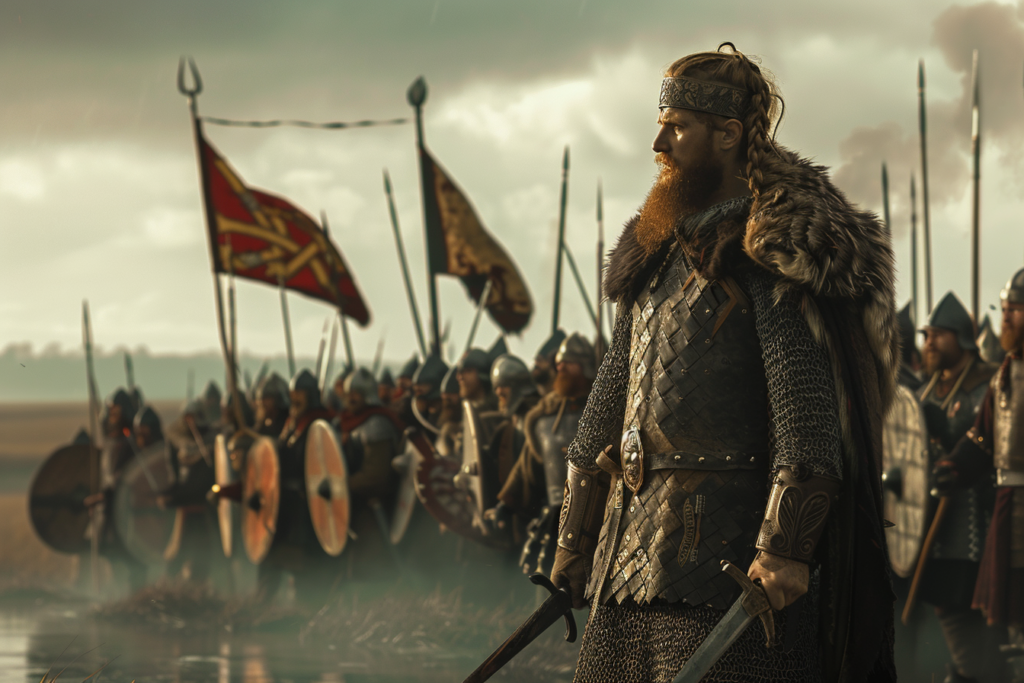

In the late 10th century, England was divided into several small kingdoms, each with its own ruler. The East Saxons were ruled by Ealdorman Brihtnoth, who was a trusted advisor to King Æthelred the Unready.
The Vikings, on the other hand, were a group of Scandinavian raiders who had been raiding the coasts of England for decades.
Tribute and Tension
The Vikings demanded tribute from the East Saxons in exchange for not raiding their lands. However, tensions were high between the two groups, as the Vikings often broke their promises and continued to raid despite receiving tribute.
Ealdorman Brihtnoth refused to pay the tribute, which further escalated the tension between the two groups.
The Viking Force
In the summer of 991, a large Viking force led by Olaf Tryggvason sailed up the River Blackwater and landed at Maldon, a small town in the kingdom of the East Saxons.
The Vikings were well-equipped and had a reputation for being fierce warriors. They had already pillaged several towns along the coast, including Folkestone, Sandwich, and Ipswich.
Despite being outnumbered, Ealdorman Brihtnoth gathered his forces and prepared to defend his land against the Viking raiders. The stage was set for a fierce battle between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons, which would go down in history as the Battle of Maldon.
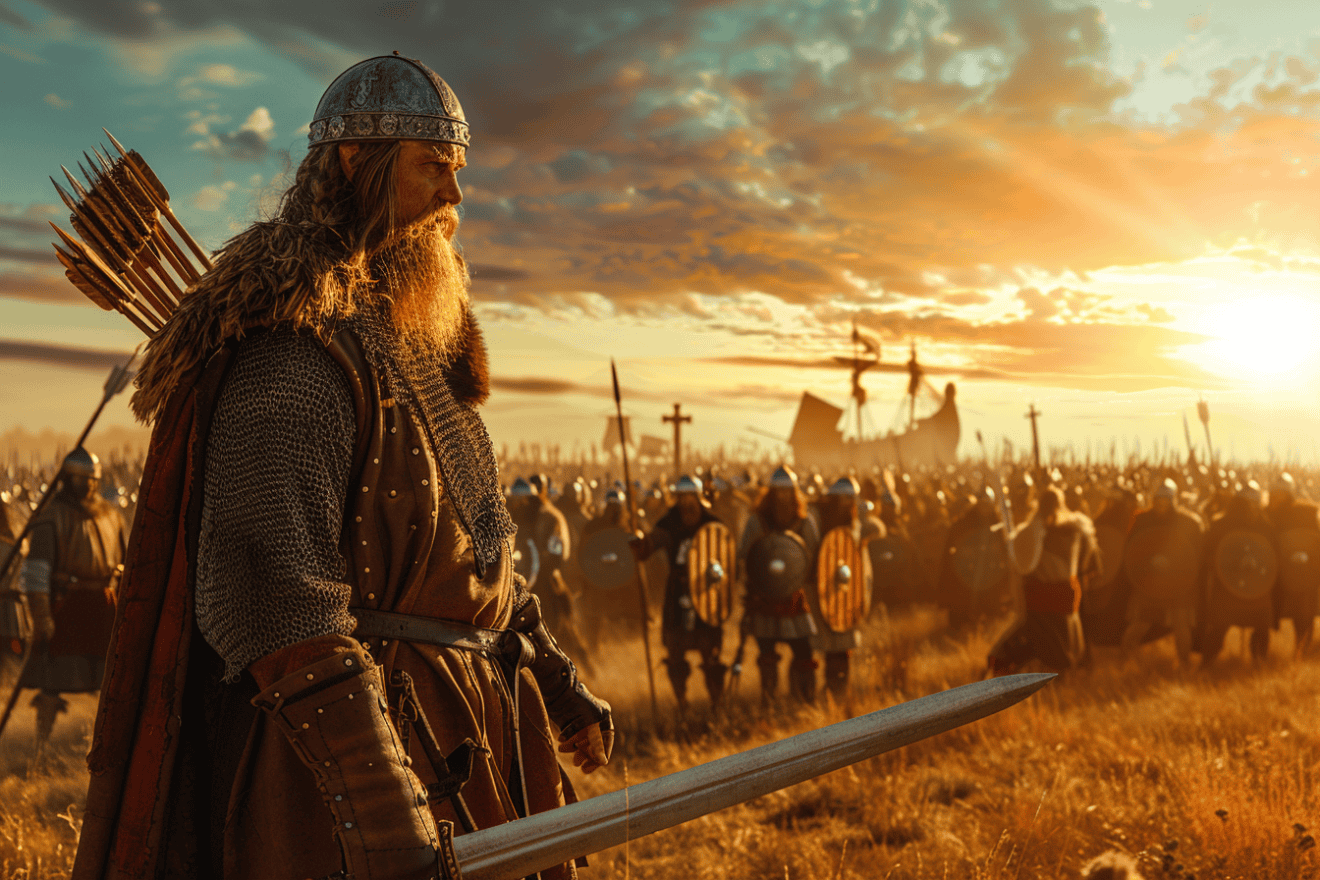
The Battle of Maldon
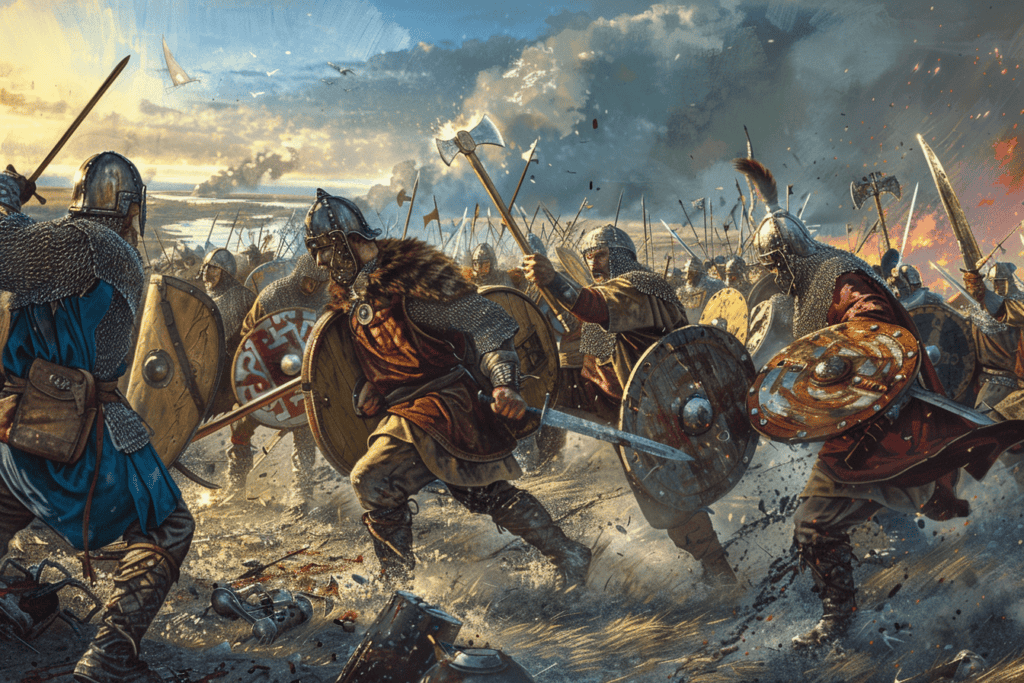

The Battle of Maldon was a fierce encounter between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons that took place in August 991 AD.
The battle was fought near the town of Maldon, in the kingdom of the East Saxons, beside the River Blackwater. The conflict is remembered as one of the most significant battles in early medieval English history and is also known for the heroic poem that was composed about it.
Combatants and Strategies
The battle was fought between the Vikings and the East Saxons led by Ealdorman Brihtnoth. The Vikings had already pillaged several towns before they were confronted by the Anglo-Saxon army.
The Vikings had a significant advantage in terms of numbers, but the Anglo-Saxons had a strong shield wall and were well-trained in the use of spears.
Key Moments of the Conflict
The battle began with a challenge from the Viking leader, who demanded that the Anglo-Saxons pay tribute to the Vikings. Ealdorman Brihtnoth refused, and the battle began.
The Anglo-Saxons fought fiercely, but the Vikings managed to break through their shield wall. Ealdorman Brihtnoth was killed in the battle, and many of his men deserted the field.
Despite the loss of their leader, the Anglo-Saxon warriors continued to fight. They managed to kill many of the Vikings before they were finally defeated. The battle was a significant victory for the Vikings, but it was also a testament to the loyalty and bravery of the Anglo-Saxon warriors.
Cultural and Religious Impact – Christianity vs. Pagan Beliefs
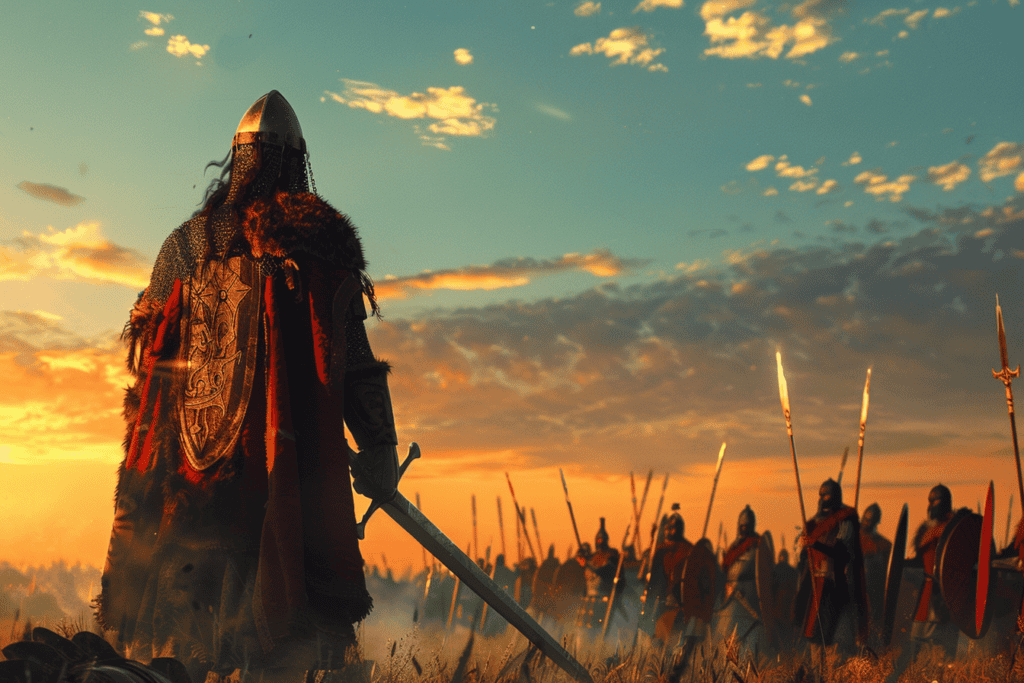

The encounter between the Vikings and Anglo-Saxons at Maldon had a significant impact on the cultural and religious beliefs of both groups. The Anglo-Saxons had already converted to Christianity, while the Vikings were still following their pagan beliefs.
The clash of these two religions resulted in a cultural shift that included new religious institutions, architectural styles, and literary traditions.
The Anglo-Saxons’ conversion to Christianity resulted in the establishment of new religious institutions, including the Church of England. The Church played a crucial role in shaping the Anglo-Saxon culture and society.
It also had a significant impact on the language and literature of the Anglo-Saxons. The Church’s influence can be seen in the Old English language, which was written in the Latin alphabet and used for religious texts.
On the other hand, the Vikings were still following their pagan beliefs, which were centered around a pantheon of gods such as Odin and Thor.
Their worship involved sacrifices and rituals that were considered barbaric by the Christians. The Vikings’ pagan beliefs had a significant impact on their culture and society, including their language and literature. The Old Norse language, which was written in runes, was used for their literature and poetry.
Influence on Language and Literature
The encounter between the Vikings and Anglo-Saxons had a significant impact on the language and literature of both groups.
The Old English language was influenced by Latin and the Church. It was used for religious texts and literature. The Anglo-Saxon literature included epic poems such as Beowulf, which is considered one of the greatest works of Anglo-Saxon literature.
The Vikings’ Old Norse language was written in runes and was used for their literature and poetry. Their literature included sagas, which were stories about their history and mythology. The sagas were passed down orally from generation to generation before being written down.
The Vikings’ literature had a significant impact on the language and literature of the Anglo-Saxons. The Anglo-Saxons were influenced by their stories and poetry.








Add Comment