Eratosthenes, an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer, is widely known for his remarkable achievement in calculating the circumference of the Earth.
Eratosthenes was born in Cyrene, a Greek colony in modern-day Libya, in 276 BCE. He later moved to Alexandria, where he became the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria, one of the most significant libraries of the ancient world.
Eratosthenes’ method of measuring the Earth’s circumference was revolutionary for his time.

He noticed that on the summer solstice, the sun was directly overhead in Syene, a city located on the Tropic of Cancer, while it was at an angle in Alexandria.
He reasoned that if the Earth was flat, the angle of the sun’s rays would be the same in both cities. However, since the Earth is round, the angle of the sun’s rays would be different.
By measuring the angle of the sun’s rays in Alexandria and knowing the distance between Alexandria and Syene, Eratosthenes was able to calculate the Earth’s circumference with remarkable accuracy.
Eratosthenes’ accomplishment in measuring the Earth’s circumference was not only a significant achievement in the field of astronomy but also in the history of science.
His method of measuring the Earth’s circumference was a crucial step in understanding the shape and size of the Earth, which later paved the way for other significant discoveries in the field of geography and cartography.
The Life of Eratosthenes

Eratosthenes was a Greek astronomer, geographer, mathematician, and poet who lived from 276-195 BCE.
He was born in Cyrene, a Greek colony in Libya, and later moved to Alexandria, where he spent most of his life.
Eratosthenes was educated in Athens and studied under some of the most prominent scholars of his time.
He moved to Alexandria, where he became the head of the Library at Alexandria, one of the greatest libraries of the ancient world.
Eratosthenes was a polymath who made significant contributions to many fields, including mathematics, geography, and astronomy.
Contributions to Mathematics and Geography
Eratosthenes is best known for his work in geography and for being the first person to calculate the circumference of the Earth.
He used his knowledge of geometry and trigonometry to measure the angle of the sun’s rays at two different locations in Egypt.
By using the difference in angle, he was able to calculate the circumference of the Earth with remarkable accuracy.
Eratosthenes also made significant contributions to mathematics.
He developed the Sieve of Eratosthenes, a method for identifying prime numbers.
This method involves creating a list of numbers and crossing out all the multiples of each prime number until only prime numbers remain.The Sieve of Eratosthenes is still used today to find prime numbers.
Eratosthenes’ work on prime numbers was groundbreaking.He realized that prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers and that they play a crucial role in mathematics.
Measuring the Earth’s Circumference – The Experiment at Syene and Alexandria
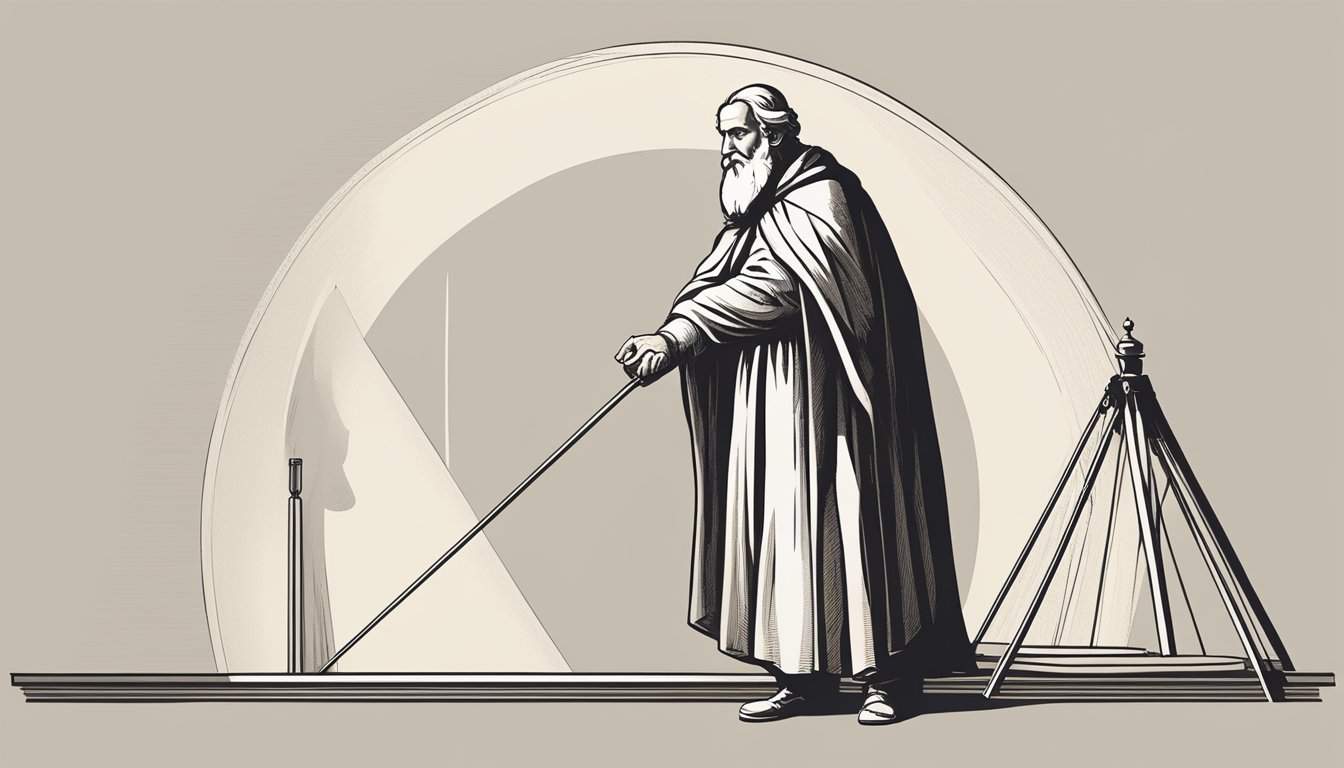
Eratosthenes’ method was relatively simple.
He first measured the angle of the sun at the summer solstice in Syene, a city located in southern Egypt.
In Syene, the sun was directly overhead, so a vertical stick cast no shadow.
Eratosthenes then measured the angle of the sun in Alexandria, a city located north of Syene. In Alexandria, a vertical stick cast a shadow.
By observing the difference between the angles, Eratosthenes was able to calculate the angle between the two cities and the distance between them.
Calculating the Circumference
Eratosthenes knew that the distance between Syene and Alexandria was approximately 5,000 stadia, a unit of length used in ancient Greece.
He also knew the approximate size of a degree of latitude, which is about 111 kilometers or 69 miles.
By dividing the distance between Syene and Alexandria by the size of a degree, Eratosthenes was able to calculate the angle between the two cities, which he found to be 7.2 degrees.
Eratosthenes then used this angle to calculate the Earth’s circumference.
He knew that 7.2 degrees was 1/50th of a circle (360 degrees), so he multiplied the distance between Syene and Alexandria by 50 to get the Earth’s circumference.
Eratosthenes’ value for the Earth’s circumference was approximately 39,375 kilometers or 24,662 miles, which is remarkably close to the modern value of 40,075 kilometers or 24,901 miles.
The Importance of Eratosthenes’ Measurement
Eratosthenes’ measurement of the Earth’s circumference was a significant achievement in the history of science and learning.
It was the first time that anyone had accurately measured the Earth’s size, and it had important implications for navigation, geodesy, and modern geography.
Eratosthenes’ method also demonstrated the power of mathematics and geometry to solve complex scientific problems.
The Legacy of Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes’ groundbreaking work in calculating the Earth’s circumference had a profound impact on later scholars and geographers.
His algorithm for measuring the Earth’s size and his contributions to the field of geography were studied and built upon by many Greek scholars, including Hipparchus, Posidonius, and Strabo.
Aristotle, who was one of the most influential philosophers of his time, was also impressed by Eratosthenes’ work and recognized its significance.
Eratosthenes’ method was used by Ptolemy, who created the Almagest, a comprehensive treatise on astronomy that was used as a standard reference for centuries.
Eratosthenes’ work also had practical applications.
Christopher Columbus, for example, used Eratosthenes’ calculations to estimate the distance of his voyage to the New World.
Eratosthenes’ algorithm was also used to measure the diameter of the Moon and to determine the longitude of different locations on Earth.
Eratosthenes’ Work in the Context of Modern Science
Eratosthenes’ work was groundbreaking not just because of the accuracy of his measurements, but also because of the scientific method he used to arrive at his calculations.
His approach to measuring the Earth’s circumference was based on empirical evidence and mathematical reasoning. His algorithm was a major step forward in the development of scientific methodology.
Eratosthenes’ work also had a significant impact on the development of chronology and the study of history. His chronographies, which were lists of events arranged in chronological order, were used to create a timeline of ancient history.
He also studied the axial tilt of the Earth and the Tropic of Cancer. His work on lunar eclipses helped to refine the accuracy of calendars.
Despite being blind for most of his life, Eratosthenes made significant contributions to the fields of mathematics, astronomy, and geography.
His work set a high standard for academic excellence. His scale of the Earth, which he developed through his project to measure the Earth’s circumference, was a remarkable achievement that continues to inspire scientists and scholars today.



Add Comment