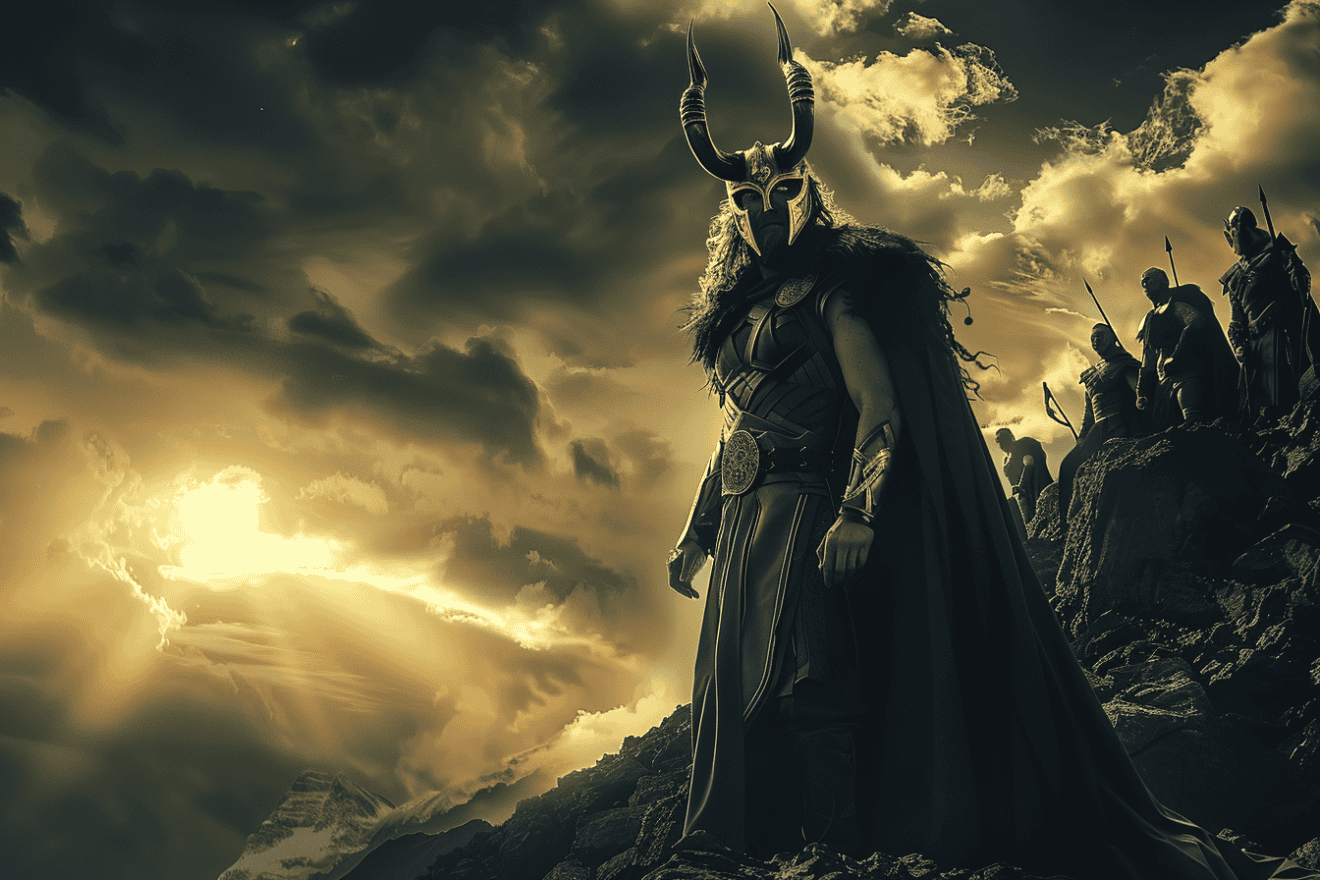
In Norse mythology, Loki is a god known for his shape-shifting abilities and cunning trickster nature. He is the offspring of giants Fárbauti and Laufey and plays a pivotal role in weaving together the Aesir gods and giants.
Loki’s character embodies chaos, and his deceptive nature often leads to turmoil, as seen in the demise of Baldr and the theft of Mjölnir.
His unparalleled shape-shifting talents blur lines of allegiance, challenging norms and shaping the mythos profoundly. This article will delve deeper into the mythology of Loki and his impact on Norse mythology.
Loki’s Origins and Family Connections

Loki’s family connections are essential to understanding his character in Norse mythology. According to the myths, Loki is the son of the giants Fárbauti and Laufey, which makes him a half-giant and half-god.
Loki’s complex blend of chaos can be traced back to his unique heritage.
Loki’s role in Norse mythology is pivotal due to his multifaceted nature and his ties to both the Aesir gods and the giants. His actions and family connections are central to understanding his place in the Norse pantheon.
Loki fathered several offspring with Sigyn and Angrboða, including Hel, Fenrir, and Jörmungandr. These eerie progeny play significant roles in Norse mythology, shaping the narrative with their presence. Hel is the goddess of the underworld, while Fenrir is a monstrous wolf and Jörmungandr is a giant sea serpent.
Loki’s Cunning and Deception

Loki is widely known as a trickster god in Norse mythology, and his cunning wit and masterful deceit are legendary. He is a shape-shifter with multifaceted abilities that allow him to outsmart even the most powerful beings.
His unpredictable nature adds to his enigmatic character, making him a fascinating figure in the pantheon of Norse deities.
One of the most notorious examples of Loki’s deceptive actions was his involvement in the death of Baldr, Odin’s beloved son. By orchestrating Baldr’s demise, Loki sowed discord among the gods, leading to chaos and conflict.
Moreover, his theft of Mjölnir, Thor’s mighty hammer, further showcases his deceptive prowess and penchant for causing mayhem.
Despite his mischievous nature, Loki’s pivotal role in Norse mythology is undeniable. His cunning and deceit add layers of complexity to the tales of gods and giants, making him an intriguing character. However, his deceptive actions have had far-reaching consequences, and his tricks often result in tragedy.
Loki’s Shape-Shifting Abilities

One of the most fascinating aspects of Loki’s character in Norse mythology is his remarkable talent for shape-shifting. He can effortlessly assume various forms, blurring the lines between ally and adversary, friend and foe.
Loki’s shape-shifting abilities allow him to transform into different animals, genders, and objects, showcasing his adaptability and resourcefulness.
Perhaps the most famous tale involving Loki’s shape-shifting is when he turned into a mare and gave birth to Sleipnir, Odin’s eight-legged horse. This act highlights Loki’s deceptive and unpredictable nature, adding layers to his character as a masterful trickster.
Loki’s ability to change forms with ease contributes to his reputation as a captivating and enigmatic character in Norse folklore. His transformations emphasize his cunning and skill for maneuvering situations with unpredictable flair, making him a figure of intrigue in the Norse pantheon.
Loki’s shape-shifting abilities are not limited to animals but also include objects and other human forms. For instance, he transformed into a salmon to escape the giant Geirrod, and he turned into a fly to distract Brokkr while he was crafting Mjolnir, Thor’s hammer. His shape-shifting abilities make him a formidable adversary and an unpredictable ally, adding to the complexity of his character in Norse mythology.
Loki’s Relationships With Norse Deities

Loki’s relationships with the Norse deities were marked by a complex web of loyalty, betrayal, and camaraderie.
In Norse mythology, Loki’s interactions with Odin and Thor were particularly noteworthy, showcasing his unpredictable nature and ability to switch allegiances for his own gain.
Despite his reputation as a trickster, Loki’s connections with deities like Odin and Thor reveal a multifaceted character capable of both loyalty and betrayal.
Loki’s Role in Key Mythological Events
Loki’s mischievous nature is evident in his involvement in several key mythological events that shape Norse mythology. His actions often bring chaos and turmoil to the divine domain, showcasing his ability to disrupt the status quo.
One of Loki’s most significant deeds was the theft of Thor’s hammer, Mjölnir. This act plunged the Norse pantheon into chaos and highlighted Loki’s ability to sow discord among the Aesir.
Moreover, Loki played a pivotal role in the death of Baldr, a beloved god. This event triggered a chain of events that led to profound consequences within the divine domain.
Loki’s kidnapping of Idun, the goddess of youth, further emphasizes his capacity for causing turmoil and unrest.
Despite his disruptive tendencies, Loki also made significant contributions to the Norse pantheon. He assisted in building Asgard’s impregnable walls, showcasing his complex nature and his significance in shaping the mythological landscape.
Loki’s Influence on Modern Culture
Loki’s influence on modern culture is undeniable, particularly in the realm of entertainment. The character has been portrayed in various forms, but it is his depiction in Marvel Comics and the Marvel Cinematic Universe that has had the most significant impact on popular culture.
Tom Hiddleston’s charismatic portrayal of Loki has garnered a massive fan following, cementing the character’s popularity in contemporary media. Audiences are drawn to Loki’s complex personality, exploring themes of redemption, antiheroism, and identity discovery.
The examination of Loki’s multifaceted nature in popular culture has transformed him into a symbol of complexity and depth, showcasing the character’s enduring relevance and magnetism in modern storytelling. Loki has become more than just a villain; he embodies the essence of an antihero with layers that continue to intrigue and captivate audiences worldwide.
While the character’s origins lie in Norse mythology, his modern-day popularity can be attributed to his portrayal in Marvel comics and the Marvel Cinematic Universe. The character’s evolution has allowed him to transcend his mythological roots, becoming a cultural icon that resonates with audiences of all ages.
Loki’s Moral Ambiguity
Loki’s character is a rich tapestry woven with the complexity of mischief and trickery. He is known for his unpredictable and morally gray decisions, which challenge traditional notions of heroism and villainy in Norse mythology.

Loki’s multifaceted nature adds layers to his character, showcasing his mischievous nature alongside moments of loyalty and helpfulness to his fellow gods. However, his actions, such as his role in Baldr’s death, reflect the depth and complexity of his character.
Loki’s intricate relationships with the gods of Asgard further highlight his unpredictable nature. His moral ambiguity becomes a central aspect of his enigmatic persona, making him a compelling figure in Norse mythology.
Loki’s Symbolism and Archetype
Loki, the Norse god of mischief, embodies the archetype of the trickster and symbolizes disruption and chaos.
His shape-shifting abilities reflect the constantly evolving nature of life and the fluidity of reality. As a trickster, Loki blurs the lines between good and evil, challenging societal norms through his transformative actions.
Loki’s deceptive nature is a reminder of the intricacies of human behavior and the fine line between order and disorder.
His essence of transformation highlights the constantly shifting landscape of existence in Norse mythology. Through his actions, he provokes thought on the duality of motives and the consequences of embracing chaos.
The god’s fluid identity, coupled with his association with fire and the hammer, reflects the unpredictable nature of life and the destructive power of transformation.
The etymology of Loki’s name, which means “fire,” underscores his relationship with this element. Additionally, Loki’s association with weapons, such as the spear Gungnir, emphasizes his role as a catalyst for change and his ability to create chaos in the world.
Loki’s Legacy in Norse Mythology
Loki, the shape-shifting trickster god, has left a lasting impact on Norse mythology. His complex relationships with other Norse deities, enigmatic nature, and involvement in key events such as the death of Baldr and the theft of Thor’s hammer, Mjölnir, solidify his position as a pivotal figure in the mythological domain.
The offspring of Loki, including Hel, Fenrir, and Jörmungandr, play significant roles in perpetuating his enduring impact on the mythological landscape. The binding of Loki as retribution for his actions not only serves as punishment, but also sets the stage for Ragnarök, the apocalyptic battle in Norse mythology. This event highlights the consequences of his trickery within the divine sphere and his lasting influence.
Loki’s legacy is a testament to the intricate and sometimes dark intricacies of the Norse pantheon. His ability to transform and deceive, coupled with his complex relationships with other gods, has made him a fascinating and enduring character in Norse mythology.






Add Comment