The Vikings were a seafaring people from the late eighth to early 11th century who originated from what is now modern-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
They are known for their raids and conquests across Europe, from Russia to Spain and even as far as North America.
Their success in battle can be attributed to their superior tactics and strategies, which allowed them to surprise and overwhelm their opponents.
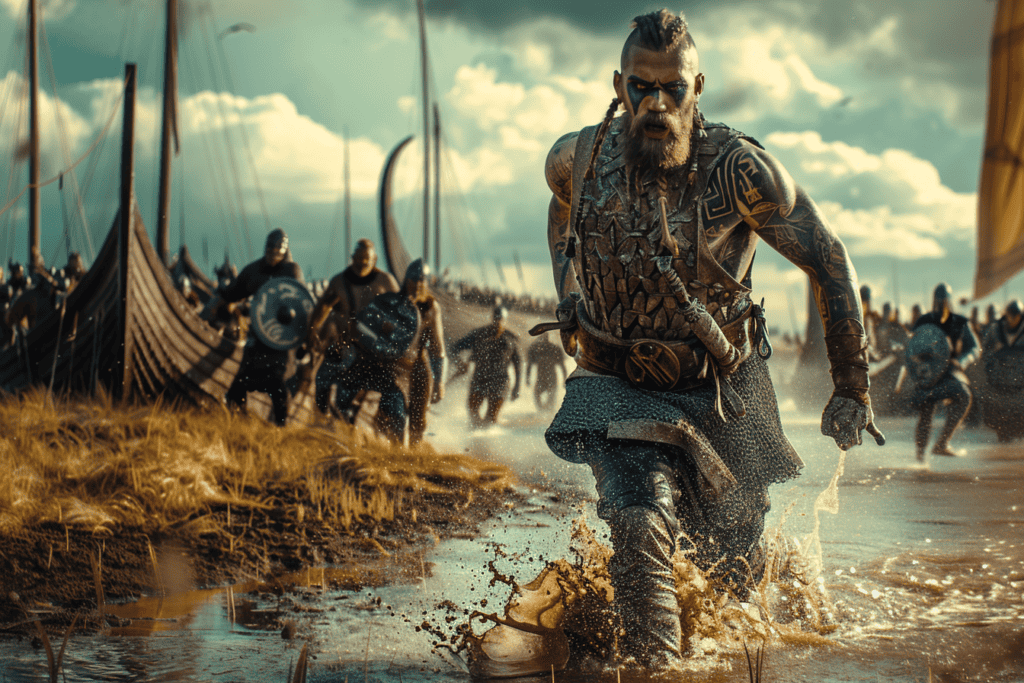
One of the key tactics used by the Vikings was the element of surprise. They would often show up at a town or monastery suddenly and without warning, loot anything they could get their hands on in short order, and then vanish in their ships before the local military forces could be mustered against them.
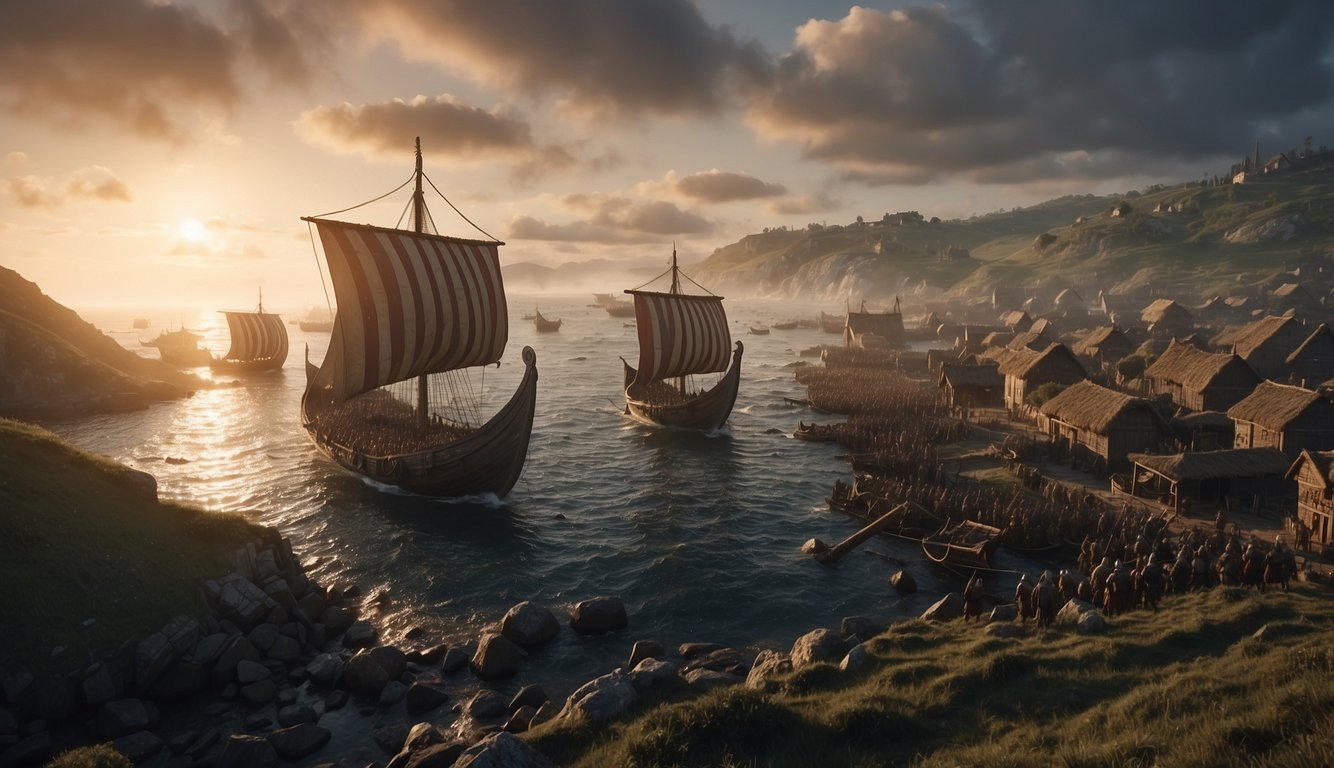
Their longships, with a characteristic shallow-draft hull, made it possible to cross the North Sea and to navigate Europe’s many rivers and appear out of nowhere, or bypass hostile land forces.
This element of surprise was used effectively in the first – and perhaps most famous – Viking raid on the wealthy monastery on the island of Lindisfarne in 793, off the coast of England.
Another tactic used by the Vikings was their superior mobility. Their ships were fast, maneuverable, and could navigate shallow waters, making them ideal for raiding and warfare.
The Vikings were also skilled at siege tactics, which allowed them to lay siege to towns and fortresses, cutting off their supplies and starving them into submission.
They would often build temporary fortifications, such as earthworks and palisades, to protect themselves from counterattacks while they were raiding or besieging a town or fortress.
Origins of Viking Raids

The Vikings were known for their raiding and pillaging of coastal towns and monasteries throughout Europe during the Viking Age (c. 793-1066 CE). This section will examine the origins of Viking raids and the tactics used by the Norse raiders.
The Viking Age began with the first recorded Viking raid on the English monastery of Lindisfarne in 793 CE.
The Vikings were a seafaring people from Scandinavia, consisting of present-day Norway, Denmark, and Sweden.
They were skilled navigators and shipbuilders, and their longships were designed for speed and maneuverability, allowing them to travel long distances and navigate shallow waters.
The Vikings were motivated to raid by a variety of factors, including a desire for wealth and land, a need for slaves, and a thirst for adventure. The harsh climate and limited resources of Scandinavia may have also played a role in driving the Vikings to seek out new lands and resources.
Viking Longship Design
The Viking longship was a key factor in the success of Viking raids. These ships were designed for speed and maneuverability, with a shallow draft that allowed them to navigate shallow waters and rivers. The longships were also equipped with a square sail and oars, allowing them to sail or row as needed.
The longships were built with overlapping planks and iron rivets, making them sturdy and seaworthy. The ships were also designed with a shallow keel and a flat bottom, allowing them to be beached for repairs or to launch a surprise attack on an unsuspecting coastal town.
Tactical Mastery in Viking Raids
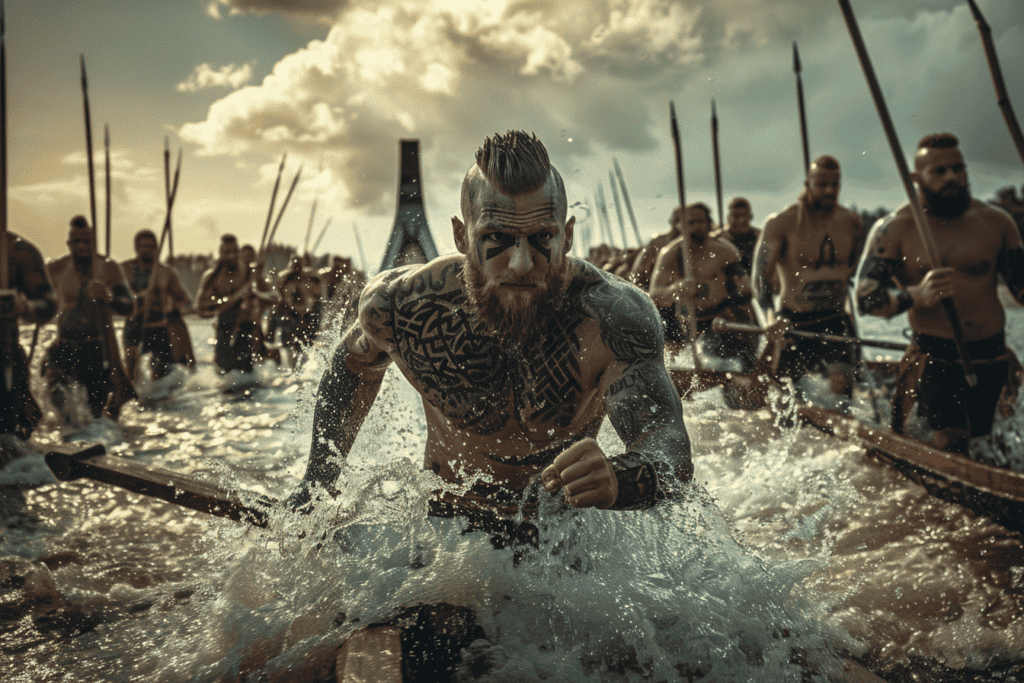

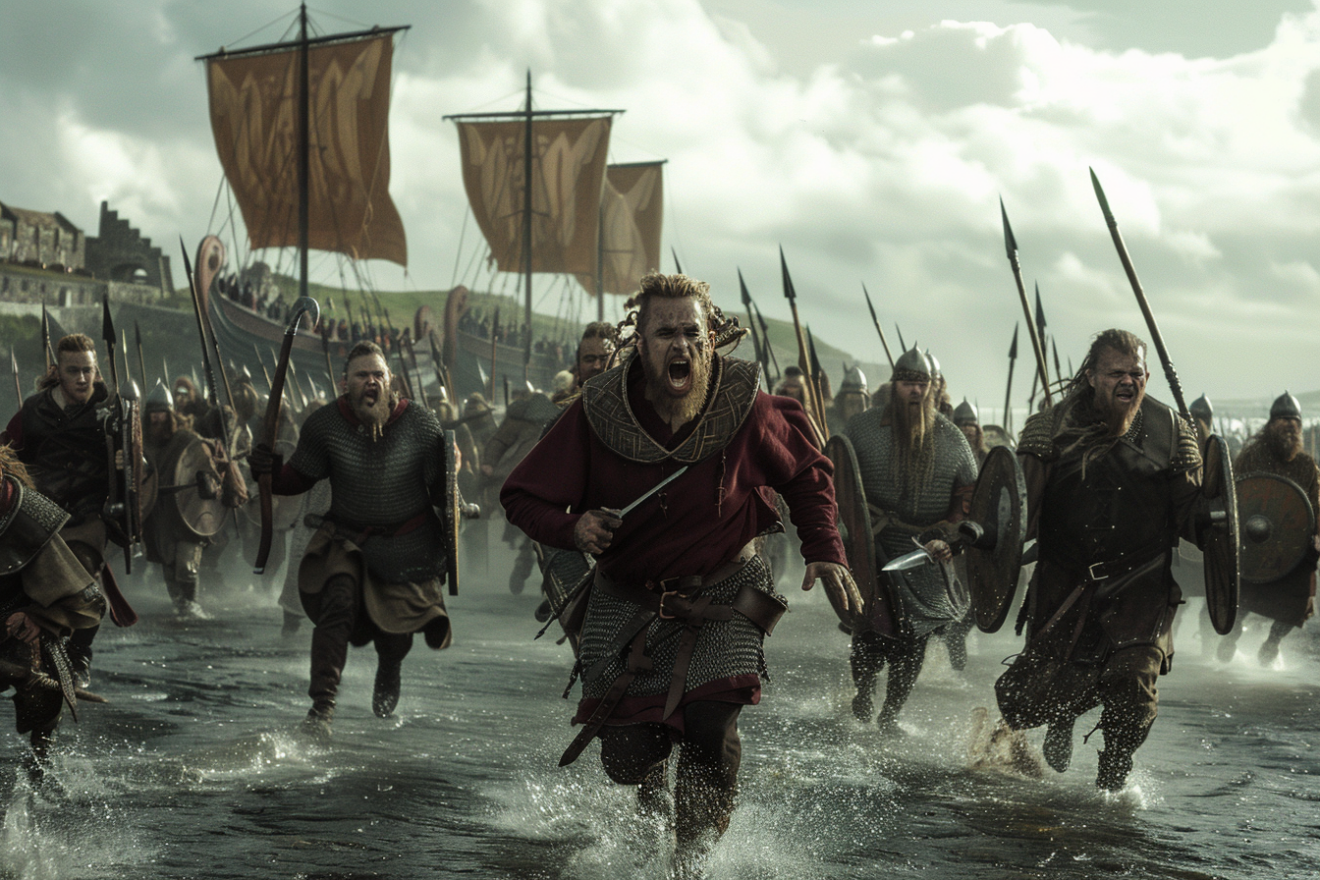
The Vikings were renowned for their military prowess and their ability to carry out successful raids on unsuspecting targets. They developed a range of tactics and strategies that allowed them to launch surprise attacks and conquer settlements.
One of the key tactics used by the Vikings was the element of surprise. They would often launch sudden raids on coastal towns and villages, catching their enemies off guard.
To achieve this, the Vikings would use their longships to sail up rivers and estuaries, allowing them to bypass coastal defenses and strike deep into enemy territory.
Another tactic used by the Vikings was to launch multiple attacks simultaneously, causing confusion and panic among their enemies. They would often split their forces into smaller groups, each with a specific target in mind. This allowed them to attack multiple targets at once, making it difficult for their enemies to mount an effective defense.
When it came to conquering settlements, the Vikings employed a range of siege tactics. They would often surround a town or fortress, cutting off its food and water supplies, and launching periodic attacks to wear down their enemies.
The Vikings were also skilled at building siege engines such as battering rams and siege towers, which they used to breach the walls of enemy fortifications. They would also use tunneling tactics to undermine the foundations of walls and towers, causing them to collapse.
Once a settlement had been conquered, the Vikings would often establish a permanent presence there. They would build fortified settlements, known as “borgs,” which would serve as bases for further raids and conquests.
Cultural and Economic Impact On Europe

The Vikings’ raids and conquests had a significant impact on the cultural and economic development of Europe.
The Vikings were skilled traders and merchants and their raids helped them acquire wealth and resources that they could use for trade.
Their raiding and trading activities helped them establish trade routes and networks across Europe. They traded a variety of goods, including furs, timber, honey, and slaves. They also established trading settlements in places like Dublin, York, and Novgorod.
In return for their goods, the Vikings received silver, gold, and other valuable items.
The Vikings’ raids also helped them acquire tribute from the European powers. The Vikings would often raid a town or city and demand tribute from the local rulers.
In some cases, the Vikings would establish a permanent presence in the area and demand tribute on a regular basis. These tributes helped the Vikings acquire wealth and resources that they could use for further conquests.
Influence on European Powers
The Vikings’ raids and conquests had a profound impact on the European powers of the time. The Vikings’ military tactics were highly effective and they were able to conquer large areas of England, Ireland, and France. The Vikings also established settlements in Iceland, Greenland, and North America.
The Vikings’ conquests helped them establish a reputation as a powerful military force. The European powers of the time began to fear the Vikings and started to take measures to defend themselves against Viking raids.
The Vikings’ conquests also had a lasting impact on the culture and language of the areas they conquered. In England, for example, the Vikings’ influence can be seen in the language, place names, and culture of the region.
Legacy of the Viking Age

The Viking Age, which lasted from the late 8th century through the 11th century, was a period of significant exploration, trade, and raiding by the Norsemen.
The Vikings, who hailed from Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, employed their maritime skills to journey around the globe, raiding and trading in Europe, Asia, and North America.
The Vikings’ impact on European society was significant. They established settlements in areas such as Normandy, which would later become a powerful duchy in France. The Vikings also played a role in the formation of the Kievan Rus, a medieval state that would eventually become Russia.
The Vikings’ influence can also be seen in the language and culture of the regions they raided and settled in. Many English words, such as “berserk” and “ransack,” have their roots in Old Norse, the language spoken by the Vikings.
Enduring Reputation and Mythology
The Vikings’ reputation as fierce warriors and raiders endures to this day. This is due in part to the mythology surrounding the Vikings, which has been popularized in modern media.
The Norse gods, such as Odin and Thor, have become well-known figures in popular culture.
The Vikings’ reputation has also been shaped by their role in history. The Viking Age was a time of significant change and upheaval in Europe, and the Vikings played a significant role in shaping the course of history during this period.
Despite their reputation as raiders and warriors, the Vikings were also skilled traders and craftsmen. Viking art, with its intricate patterns and abstracted animal forms, is highly regarded today.
The Vikings’ impact on European history is undeniable. Their legacy can be seen in the language, culture, and mythology of the regions they raided and settled in.









Add Comment