The Vikings, often stereotyped as brutal warriors, had a rich spiritual life. They did, in fact, pray, and their beliefs were deeply rooted in Norse Paganism.
Their pantheon of gods, including Odin, Thor, and Freyja, played a significant role in their daily lives. But what sparked their devotion to these deities?
What rituals and practices did they use to connect with their gods? The Vikings’ spiritual beliefs and values are more complex than they’re often given credit for, and it’s clear that their faith was deeply intertwined with their culture and daily life. But what lay at the heart of their beliefs?
The Gods of Norse Paganism

Worshiping a diverse pantheon of deities, Norse pagans believed in the existence of multiple gods and goddesses, each with their own distinct powers and domains. At the forefront was Odin, the All-Father, known for his wisdom and cunning. He was often depicted as a bearded man wearing a wide-brimmed hat and carrying a spear.
Thor, the god of thunder, was revered for his strength and bravery, wielding a mighty hammer called Mjolnir. Freyja, the goddess of love and fertility, was associated with beauty, war, and death. The Norse pantheon also included Tyr, the god of law and justice, Baldur, the god of light and purity, and Loki, the trickster god.
These deities were believed to inhabit the nine worlds of the Norse cosmos, including Asgard, Midgard, and Jotunheim. Norse pagans believed that the gods and goddesses intervened in human affairs, influencing the course of battles, harvests, and individual lives.
This complex network of divine beings shaped the Vikings’ worldview and informed their daily practices and decisions.
Rituals and Practices of Worship

As they sought to honor and appease their gods, the Vikings engaged in various rituals and practices that reflected their belief in the divine intervention. They believed that their gods and goddesses required regular offerings and sacrifices to maintain harmony and balance in the world.
To achieve this, the Vikings conducted rituals and ceremonies, often at sacred sites such as temples, shrines, and burial mounds. These rituals typically involved the offering of food, drink, and other items, which were believed to be consumed by the gods. In some cases, human sacrifices were made, often as a way to appease the gods and secure victory in battle or protection from natural disasters.
The Vikings also practiced divination, seeking guidance from the gods through various means, including the reading of omens and the casting of lots. Moreover, they believed in the importance of maintaining social and cultural norms, such as respect for elders and the following of traditional customs and laws.
Viking Spiritual Beliefs and Values

Throughout their society, the Vikings held a complex and multilayered spiritual worldview that emphasized the importance of honor, courage, and loyalty. Their spiritual beliefs were deeply intertwined with their daily lives, influencing their values, morals, and social norms.
The Vikings believed in a concept called ‘wyrd,’ which referred to the web of fate that connected all beings and events. This belief in a predetermined destiny instilled a sense of responsibility and accountability among the Viking people.
In addition to their belief in wyrd, the Vikings also placed great value on personal and family honor. They believed that an individual’s reputation and honor were reflected in their actions and deeds, and that a good reputation was essential for a successful and prosperous life.
This emphasis on honor and loyalty also extended to their relationships with others, both within their communities and in their dealings with outsiders. The Vikings’ spiritual beliefs and values were, consequently, deeply rooted in their social and cultural practices, and played a significant role in shaping their daily lives and interactions.
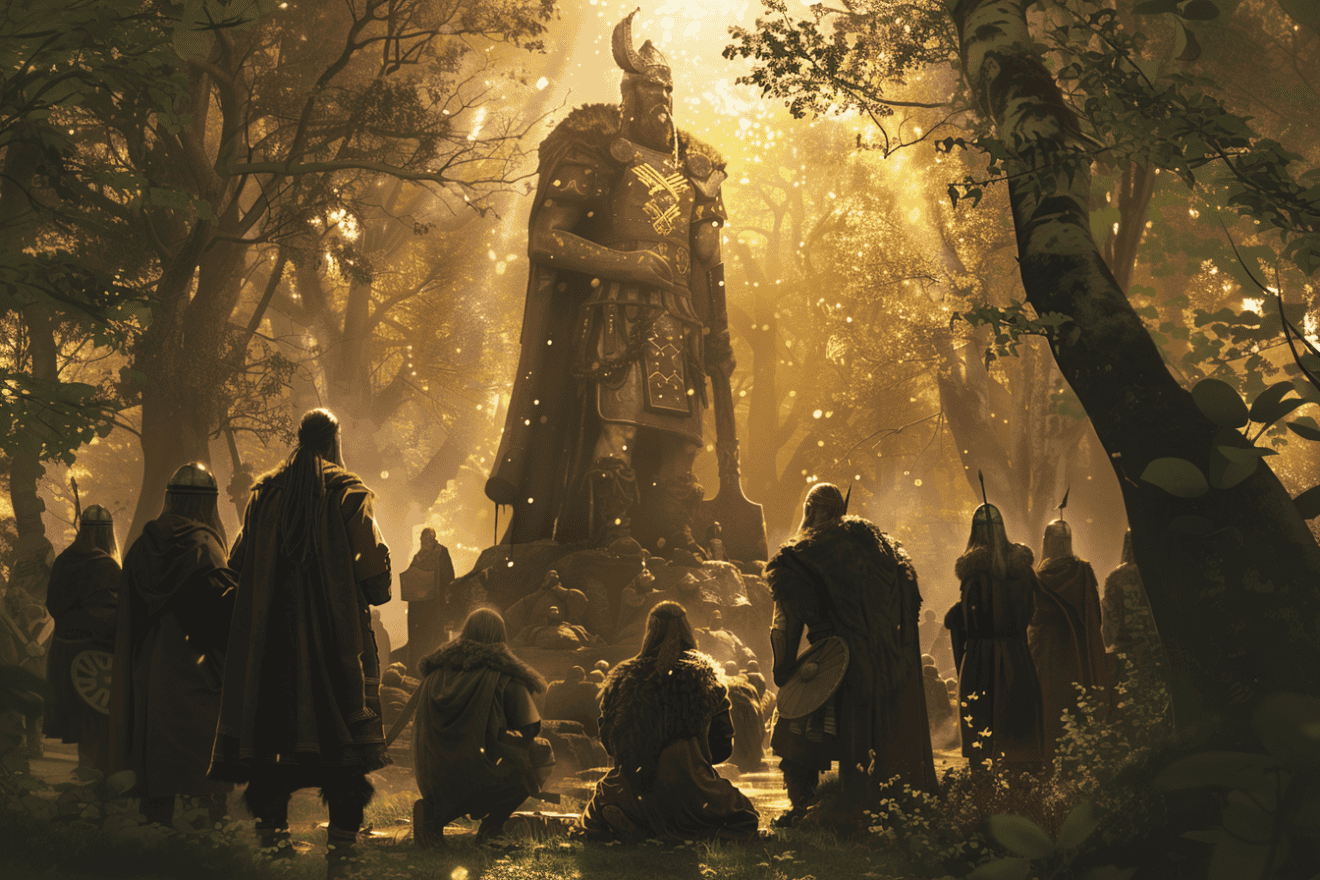
Gods and Goddesses of Asgard

The Vikings’ spiritual beliefs and values were also reflected in their reverence for the gods and goddesses of Asgard, who they believed actively intervened in their daily lives. The Aesir gods, led by Odin, the All-Father, and the Vanir gods, led by Frey, were considered to be powerful beings that controlled the forces of nature and human destiny.
The Vikings believed that these gods and goddesses influenced their lives in various ways, from the outcome of battles to the fertility of the land. Among the most prominent gods and goddesses were Thor, the god of thunder, Freyja, the goddess of love and fertility, and Tyr, the god of law and justice.
The Vikings also revered the goddess Hel, who ruled over the underworld, and the trickster god Loki, who was known for his cunning and mischievous ways. The Vikings believed that these gods and goddesses could be appeased through offerings, sacrifices, and rituals, and that they could provide protection, guidance, and wisdom to those who worshipped them.
The complex pantheon of gods and goddesses in Asgard played a central role in the Vikings’ spiritual lives, influencing their daily practices, beliefs, and values.
The Role of Priests and Shamans
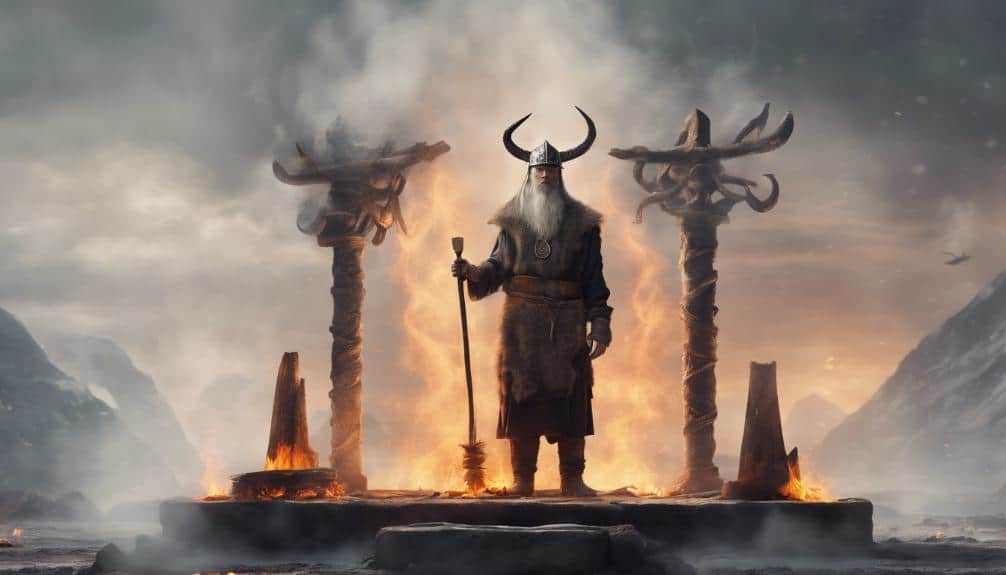

Viking priests and shamans, chosen by the gods themselves, acted as mediators between the mortal world and the domain of the gods. They played a vital role in Viking religious practices, performing rituals and sacrifices to secure the gods’ favor. These spiritual leaders were also responsible for interpreting the gods’ will, often through divination and omens. They’d advise chieftains and warriors on matters of war, agriculture, and commerce, guiding them to make decisions that aligned with the gods’ desires.
In Viking society, priests and shamans held significant social standing, often ranking alongside chieftains and warriors. They were knowledgeable in the ancient myths and legends, and could recite the poetic Eddas from memory. These spiritual leaders would also lead ceremonies and feasts, offering sacrifices to the gods and ensuring the community’s spiritual well-being.
Through their mediation, the Vikings believed they could maintain balance and harmony in their lives, as well as secure the gods’ protection and blessings.









Add Comment