In Viking society, women enjoyed remarkable rights. They could divorce, own land, and inherit property.
Economic independence elevated their status, allowing them to advocate in legal matters. Women in Norse society challenged gender norms, showcasing their importance.
Marital autonomy and property rights empowered Viking women, highlighting their roles as decision-makers. Beyond homemaking, they engaged in trade, religious ceremonies, and even warfare.
Female warriors like Lagertha and Freydis Eiriksdottir redefined gender roles with their leadership. The influence of Viking women reshaped societal dynamics greatly, hinting at their far-reaching impact.
Women’s Legal Rights in Viking Society
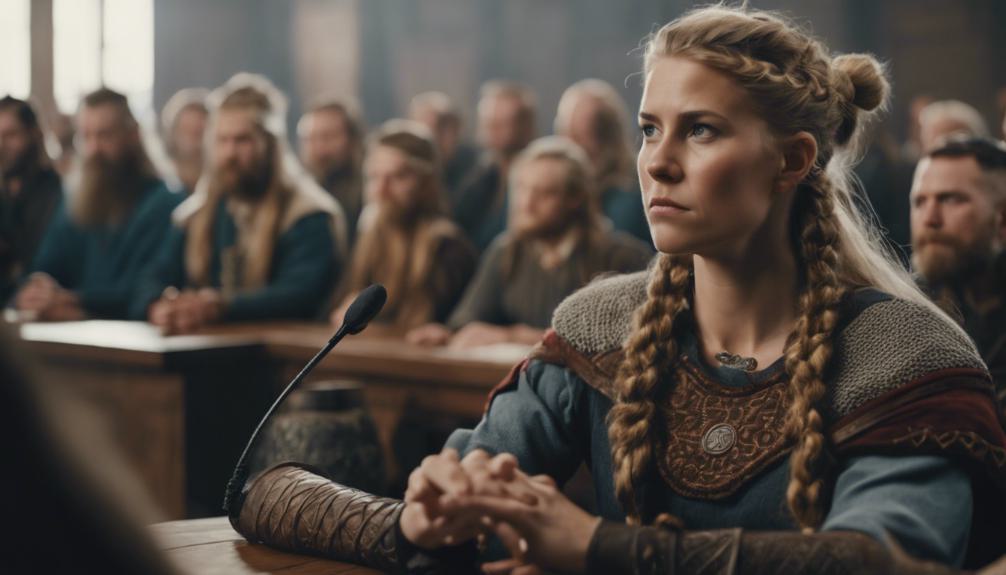

Viking women enjoyed significant legal autonomy within their society, challenging traditional norms and asserting their rights in marriage and property ownership. In Viking society, women had the right to divorce their husbands under specific conditions, a privilege not commonly seen in other contemporary cultures. This right to divorce granted Viking women a level of agency and control over their own lives that was quite progressive for the time.
Furthermore, they had substantial economic independence as they could own and inherit property, including valuable assets like land and livestock. This economic autonomy not only provided financial security but also elevated their status within the community.
In addition, Viking women played a key role as legal advocates, being able to bring matters before the assembly and actively participate in legal affairs. By exercising these rights and challenging gender norms, Viking women showcased their importance and influence in shaping Viking society.
Property and Inheritance for Viking Women
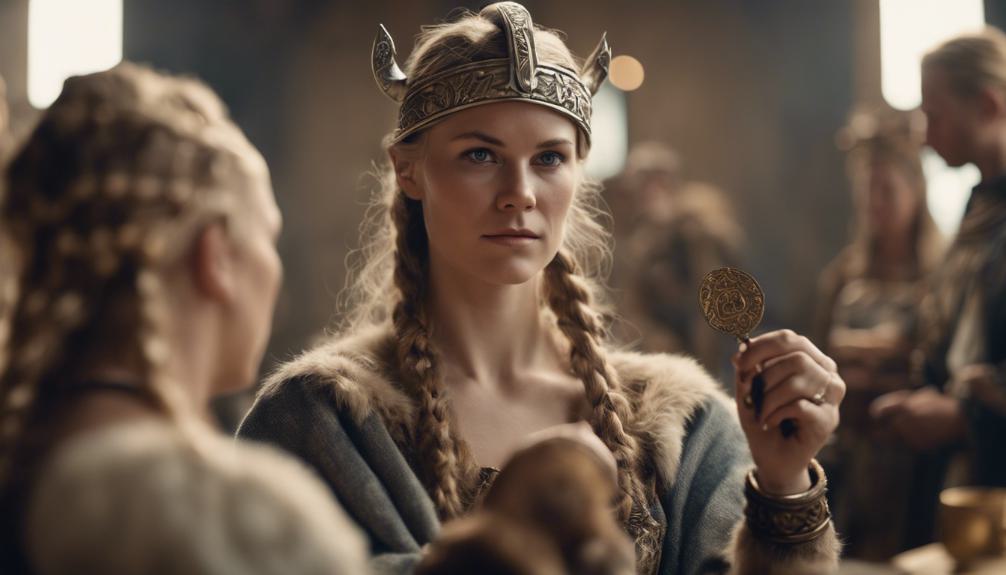

Amidst the intricate legal framework of Viking society, women’s autonomy and economic independence were particularly exemplified through their right to own and inherit property, including valuable assets like land and livestock. In Viking culture, property rights weren’t solely reserved for men; women also held the right to own and manage their own estates, providing them with a sense of financial security and independence.
Upon the death of a husband, Viking women were entitled to a portion of his estate, ensuring their inheritance rights were recognized and protected. Additionally, women in Viking society could act as legal advocates, bringing forth matters before the assembly and actively participating in legal affairs, showcasing their autonomy and role in decision-making processes.
The ability for Viking women to retain their dowry, exercise divorce rights based on neglect or violence, and have judicial independence illustrated their legal autonomy and protection within a patriarchal society.
Marriage and Family Life of Viking Women
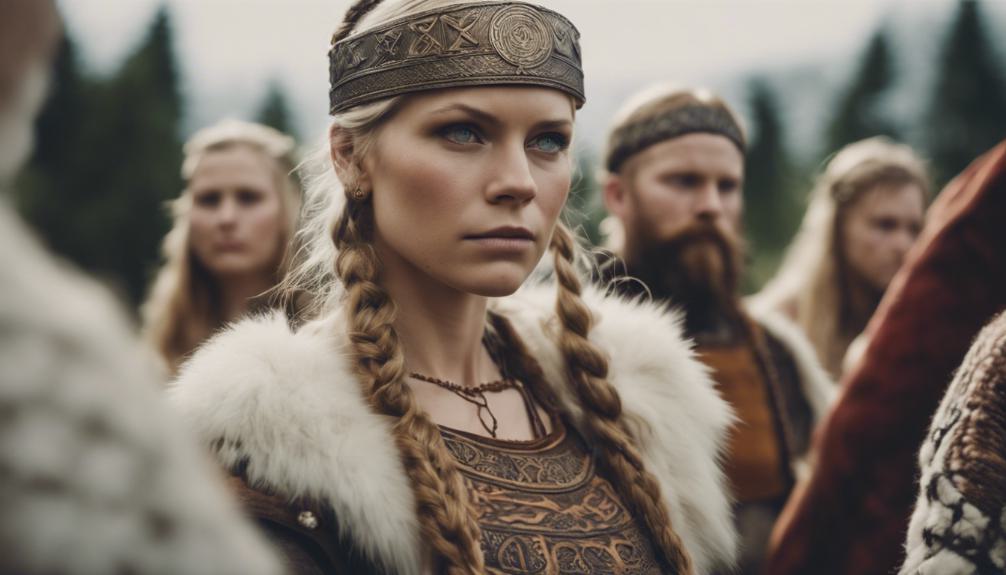

With their autonomy in choosing partners and ability to dissolve marriages under specific circumstances, Viking women navigated marriage and family life with agency and influence. In Viking society, women held significant roles in managing households, making strategic decisions, and overseeing the arrangements of marriages. They weren’t just passive participants but active decision-makers, respected for their contributions.
Women wielded authority and often represented their families in legal disputes, showcasing their judicial independence and importance within the community. Even young girls in Viking culture were knowledgeable about selecting suitable husbands, highlighting their agency in making marital decisions from a young age. The respect and leverage Viking women held in marriage and family life were evident, as they played a vital role in shaping the dynamics of their households and communities.
Gender Roles in Viking Culture
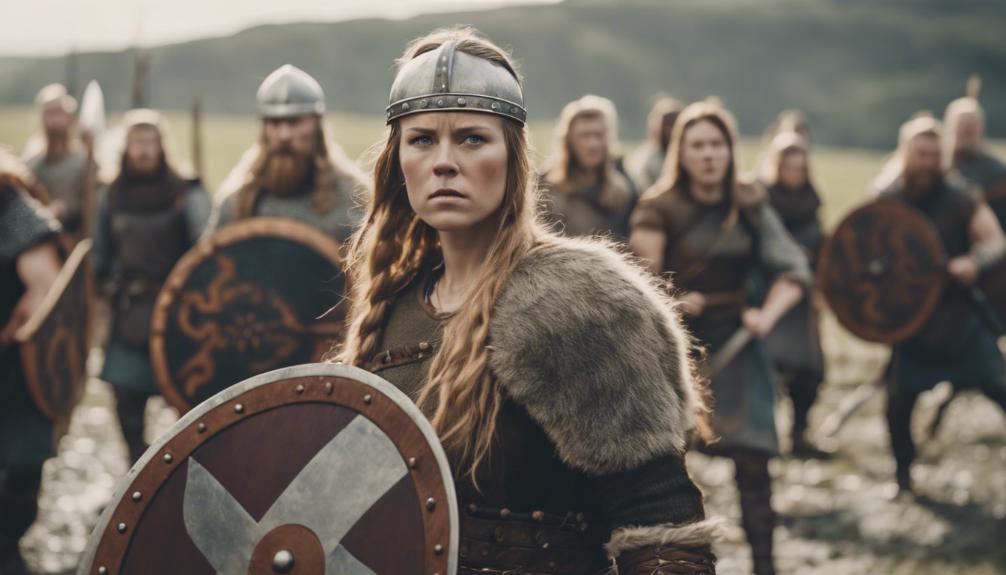

Women in Viking culture held a diverse array of roles, extending far beyond traditional homemaking duties. During the Viking Age, gender roles were more fluid than in many other contemporary societies. Viking women weren’t confined to the domestic sphere; they were active participants in various aspects of society. Besides managing estates and engaging in trade, they also played vital roles in religious ceremonies.
Archaeological evidence and Norse sagas depict women as shieldmaidens and warrior women, standing shoulder to shoulder with men in battles. These warrior women weren’t mere legend; they were real historical figures who wielded weapons and fought alongside their male counterparts. In addition to their roles in warfare, Viking women were healers, seers, weavers, metalworkers, and priestesses. They had autonomy, represented their families in legal disputes, and nurtured the next generation.
Mothers were responsible for educating children and passing down cultural traditions, showcasing the important roles women played in Viking society beyond traditional gender norms.
Viking Women Warriors History
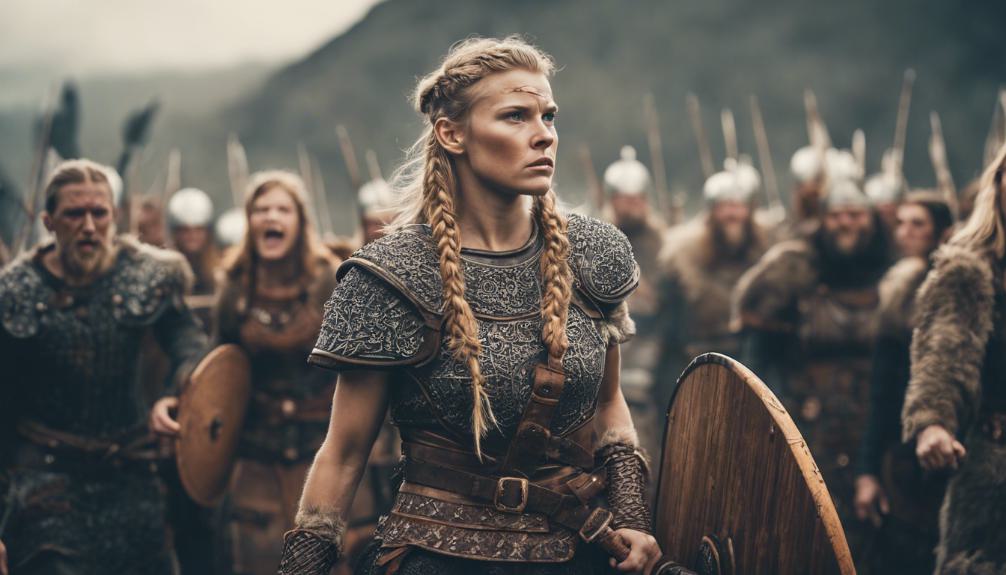

Gender roles in Viking society were more flexible than commonly believed, evident in the historical accounts of female warriors actively participating in battles alongside men. Recent archaeological finds have provided compelling evidence of Viking women warriors during the Viking period. These Norse women not only fought in battles but also held significant societal roles beyond combat, including leadership and strategic planning. The sagas and tales of the Vikings often romanticize shieldmaidens, reflecting the societal acceptance of female warriors and their importance in Norse culture.
Legendary Viking women warriors, such as Lagertha and Freydis Eiriksdottir, are celebrated for their bravery and leadership in battle, challenging traditional gender roles. These women weren’t simply exceptions but rather exemplars of a broader trend of female participation in warfare during the Viking era. Their stories serve as a confirmation to the remarkable history of Viking women warriors and their impact on shaping gender roles in Viking society.
Key Takeaways on Viking Women’s Rights
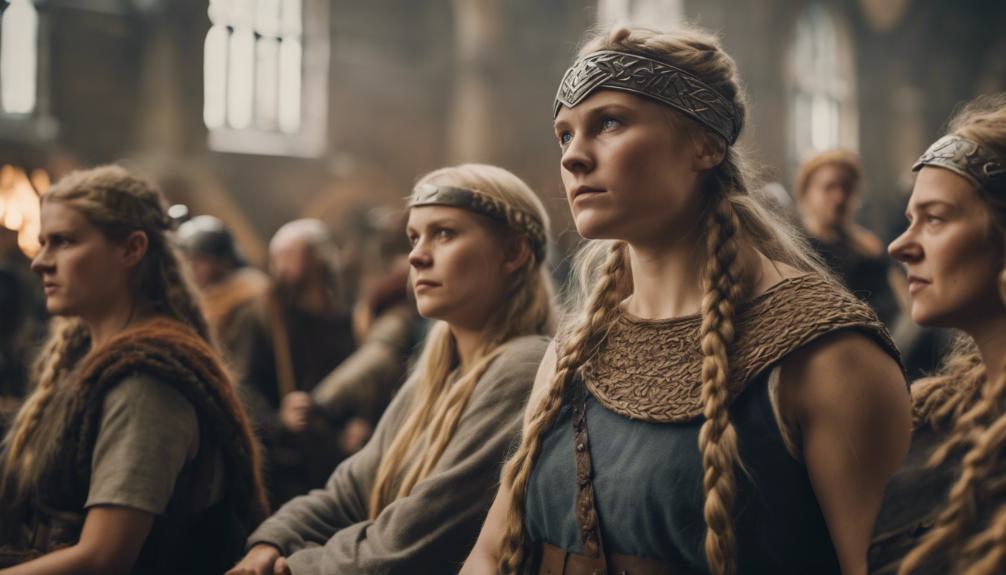

Having legal autonomy and protection, Viking women enjoyed significant rights in society that challenged traditional norms. Viking women had the legal right to divorce under specific circumstances, allowing them to retain their dowry. They could also own and inherit property, including valuable assets like land and livestock.
In the event of their husband’s passing, Viking women were entitled to a portion of his estate, demonstrating their legal autonomy and financial independence. Remarkably, these women could act as legal advocates, presenting cases before the assembly and actively participating in legal proceedings. The Icelandic sagas provide insights into the rights and roles of Viking women, portraying them as strong and empowered individuals.
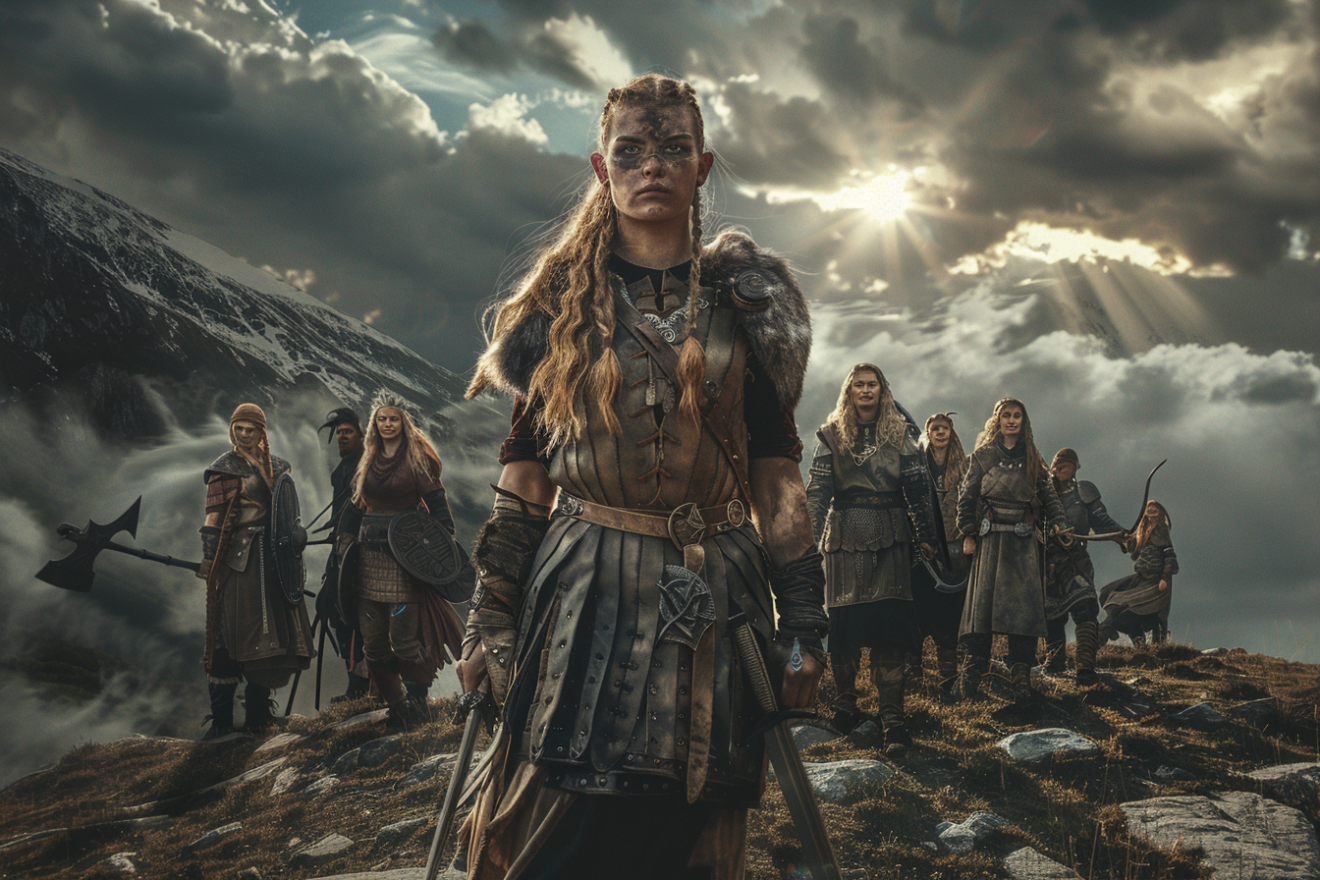
Furthermore, grave goods found in burials suggest that women held esteemed positions in society, as they were often buried with valuable items such as household utensils. Overall, Viking women’s rights showcased a level of autonomy and influence that was ahead of their time, challenging traditional gender norms in remarkable ways.








Add Comment